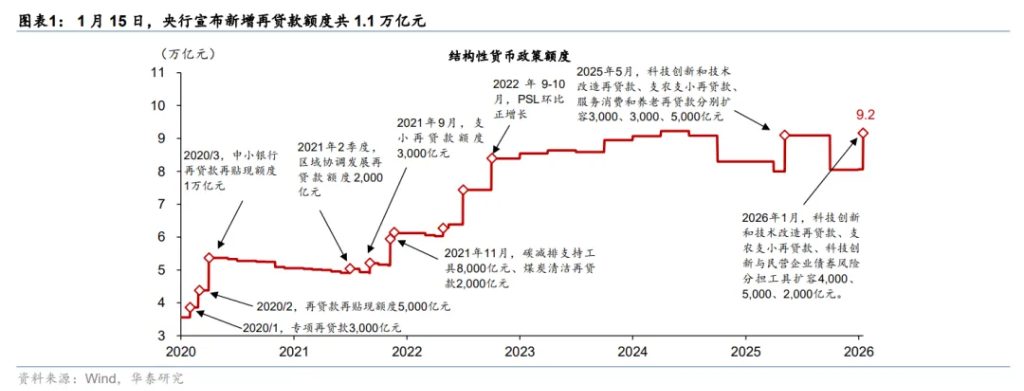
Yesterday, the central bank introduced eight structural monetary policy measures, sending a strong signal of stabilizing growth. The core measures include reducing the interest rates of various structural monetary policy tools by 0.25 percentage points and expanding the total quota of structural tools by approximately 1.1 trillion yuan. The central bank explicitly stated that, looking at this year, there is still “some room” for reserve requirement ratio (RRR) cuts and interest rate reductions. The statutory deposit reserve ratio, currently at 6.3%, still has room for reduction, and constraints from exchange rates and net interest margins have weakened. Analysts believe that this is a “structural interest rate cut” that balances internal and external equilibria, with a 50-basis-point RRR cut expected to be implemented in the first quarter.
A press conference held by the State Council Information Office at 3:00 PM on January 15, 2026, became the focus of attention in the capital markets.
On the same day that the financial data for December 2025 was released, the central bank implemented a set of 'combined measures.' In response to the market's demand for liquidity, the central bank did not directly adjust the OMO (Open Market Operations) interest rate but instead opted for a more precise approach—structural interest rate cuts.
 At the press conference, the People's Bank of China announced the introduction of eight structural monetary policy measures and explicitly stated that there is still some room for reductions in reserve requirements and interest rates this year.
At the press conference, the People's Bank of China announced the introduction of eight structural monetary policy measures and explicitly stated that there is still some room for reductions in reserve requirements and interest rates this year.
Structural 'Interest Rate Cuts' Take the Lead
The most significant announcement at the press conference was related to the adjustment of 'prices.'
The central bank announced a 0.25 percentage point reduction in the interest rates of various structural monetary policy tools. Specifically, the one-year relending rate was reduced from the current 1.5% to 1.25%, with corresponding adjustments to other maturity tiers; the rediscount rate was lowered from 1.75% to 1.5%.
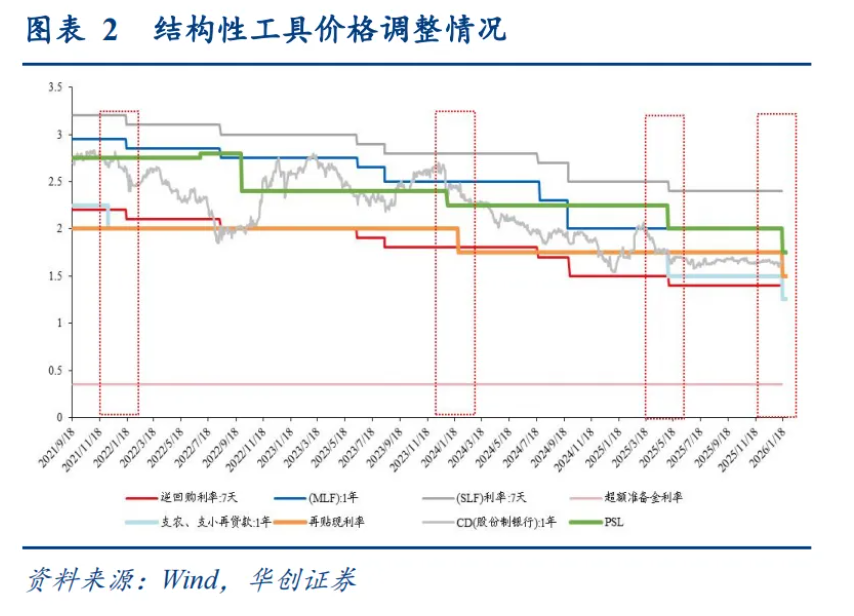
This is not a comprehensive interest rate cut, but under the current economic conditions, its signaling significance cannot be overlooked.
According to Hua Chuang Securities analysis, considering historical precedents, standalone adjustments to structural tools occurred in December 2021 and January 2024 when the OMO or MLF rates remained unchanged.
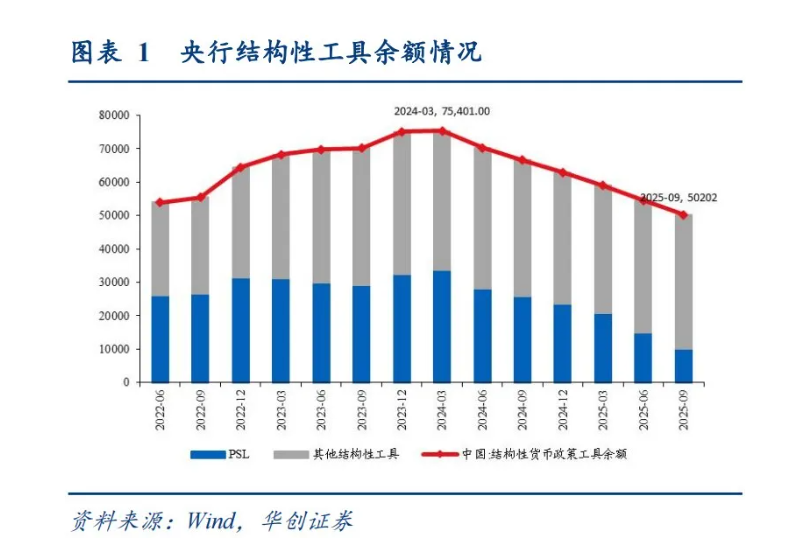
From the perspective of cost reduction, as of the end of the third quarter of 2025, the balance of structural monetary policy tools stood at approximately 5.4 trillion yuan. China Galaxy Macro estimates that this reduction will save banks about 13.5 billion yuan in costs.

The Guotai Junan Macro team believes that this represents a 'structurally balanced interest rate cut that considers both domestic and external equilibriums.' Internally, prices related to domestic demand remain weak, requiring stronger policy support; externally, the divergence in the U.S. economy has kept Treasury yields high. The central bank’s use of structural interest rate cuts 'effectively supports the resilience of the domestic economy while continuing the trend of RMB appreciation.'
Implementation of eight measures
In addition to the decline in prices, there is also an expansion in quantity. The central bank introduced eight specific measures at this press conference, focusing on boosting domestic demand, technological innovation, and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
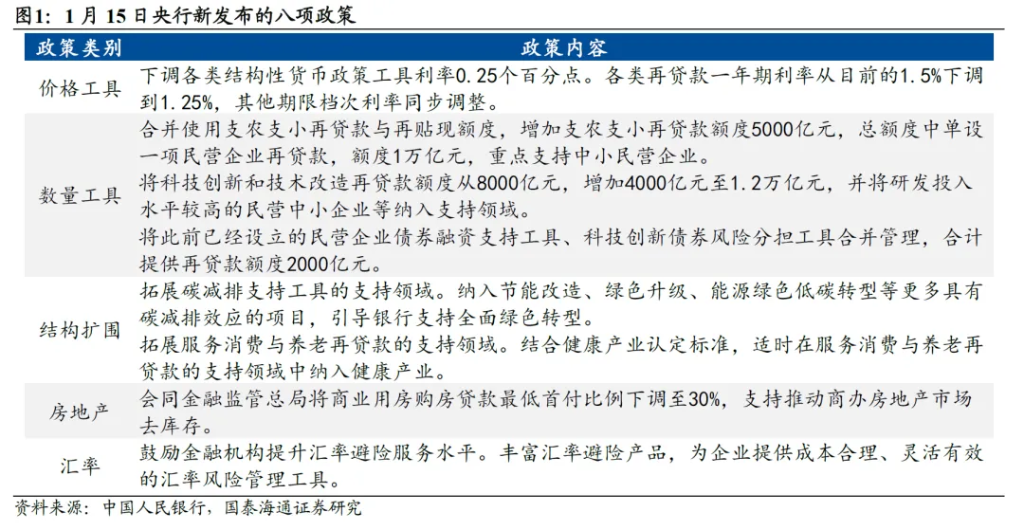
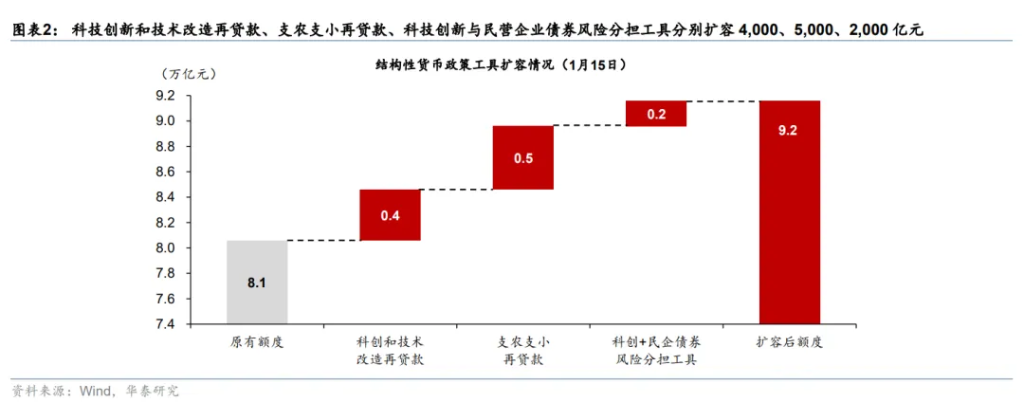
According to Huatai Securities' quantitative breakdown, the central bank has added approximately 1.1 trillion yuan in relending quotas. How will this funding be allocated?
Support for agriculture, small businesses, and private enterprises: Integration of relending for agriculture and small businesses with rediscounting, increasing the quota by 500 billion yuan; additionally, a separate relending quota of 1 trillion yuan specifically for private enterprises has been established within the total quota (incorporated into both existing and new quota consolidations).
Technological innovation: An increase of 400 billion yuan in relending quotas for technological innovation and technical transformation, raising the total to 1.2 trillion yuan.
Bond support: Consolidation of tools to establish risk-sharing mechanisms for bonds issued by technology innovation and private enterprises, providing a relending quota of 200 billion yuan.
Zhong Linnan of GF Macro pointed out that introducing structural tool reforms during the peak season for Q1 credit deployment helps maximize the structural adjustment function of monetary policy. The integration and consolidation of tools aim to 'reduce operational costs of policies and avoid redundancy of policy resources.'
Notably, further easing has been implemented in the real estate sector. The central bank, together with the Financial Regulatory Authority, announced a reduction in the minimum down payment ratio for commercial property mortgage loans to 30%. Huatai Securities’ analysis suggests that this will marginally improve demand for commercial real estate and promote destocking in the commercial office real estate market.
How soon will comprehensive reserve requirement ratio (RRR) cuts and interest rate reductions occur?
Structural easing has already been implemented, but the market is more concerned about when the 'big move' in terms of aggregate measures will come.
At the press conference, the central bank provided very clear forward guidance. Relevant officials from the central bank explicitly mentioned: "Regarding the reduction of reserve requirements and interest rates, there is still some room for adjustment this year."
China Galaxy Macro Analysis believes this signals a clear easing of monetary policy. The central bank pointed out that the average level of required reserve ratios for financial institutions is currently 6.3%, and "there is still room for reduction."
As for constraints on interest rate cuts, they seem to be easing. The central bank noted that factors such as exchange rates and net interest margins, which might restrict comprehensive interest rate cuts, have shown improvement.
Exchange Rate Aspect: The RMB exchange rate has remained relatively stable, the US dollar is in a rate-cutting cycle, and the exchange rate does not pose a strong constraint.
Net Interest Margin Aspect: Since 2025, signs of stabilization in banks’ net interest margins have emerged, and in 2026, a significant amount of long-term deposits will mature for repricing.
In this regard, Guangfa Macro provided a rational forecast: Constraints on reducing reserve requirements and interest rates are indeed decreasing, but from a practical operational perspective, it is estimated that the conditions for interest rate and reserve requirement cuts in 2026 can refer to 2025, i.e., **"reserved for when necessity arises,"** and excessive short-term speculation should be avoided.
China Galaxy Macro offered a more specific prediction: “A 50-basis-point reduction in reserve requirements in the first quarter remains likely,” to maintain ample liquidity in support of government bond issuance; while a comprehensive interest rate cut still needs to await the right timing, with an expected one to two interest rate cuts throughout the year, totaling a reduction of 10-20 basis points in policy rates.

New Policy Direction: Is DR001 Becoming the New Benchmark?
There was another detail in the press conference that was easily overlooked but carried significant professional value.
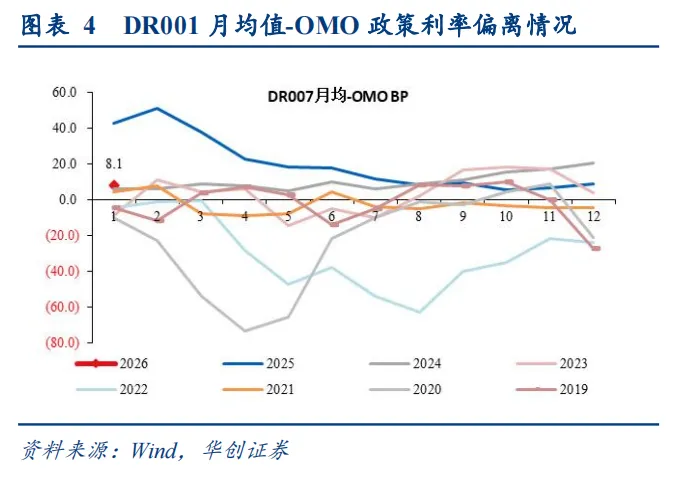
Guangfa Macro astutely noted that this meeting explicitly stated for the first time “to guide overnight interest rates to operate near the level of policy rates.”

Previously, the central bank often stated that it would 'guide market interest rates to fluctuate around the policy rate.' The market typically assumed this 'market interest rate' referred to DR007 (the 7-day repo rate). However, this time, the central bank explicitly pointed to DR001 (the overnight rate).
What does this mean? Hua Chuang Securities analyzed that since the reform of the monetary policy framework in 2024, the central bank's willingness and ability to manage the short end have significantly strengthened. Explicitly guiding the overnight rate 'helps stabilize expectations in the money market.' As high-interest deposits flow back, the tightening of liquidity may remain relatively controllable.

The 'spring rally' in the bond and stock markets
With favorable policies blowing toward the market, what does this mean for various asset classes?
Bond Market: Hua Chuang Securities noted that the meeting mentioned the 10-year government bond yield had recently stabilized around 1.8%-1.9%, which the central bank views as a 'stable and healthy operation of the bond market.' This implies that the regulatory-approved trading range has shifted upward, and the central bank’s 'desired range' may dynamically adjust based on market conditions. China Galaxy Securities expects the 10-year government bond yield to remain between 1.6% and 1.9%, with an overall trend of higher yields earlier and lower yields later.
Stock Market: China Galaxy Securities’ macroeconomic team believes that investing in the Chinese stock market could yield excess returns, emphasizing the 'spring rally' investment opportunity. The reasons include: the central bank once again signaling an easing of monetary policy; the appreciation of the renminbi driving down asset risk premiums; and capital markets spurring household deposit reallocation.
Exchange Rate: According to Morning FX data, December's foreign exchange settlement figures were 'explosive,' reaching record highs, while the RMB CFETS Index rose. China Galaxy Securities predicts that the renminbi exchange rate will experience steady, moderate appreciation in 2026, approaching 6.9 by year-end.
A strong economic 'start to the year' is worth anticipating.
Monetary policy in 2026 has begun with a 'structural interest rate cut.'
As Guotai Junan noted, this was an operation that 'balanced domestic and external equilibria.' By lowering interest rates on structural tools and expanding their quotas, the central bank took preemptive measures to stabilize growth and adjust structures. At the same time, it explicitly preserved room for broader reserve requirement ratio cuts and interest rate reductions, ensuring sufficient ammunition to address future uncertainties.
Against the backdrop of proactive fiscal policy and highly coordinated monetary policy, China's economy is poised for a strong start in 2026, which is highly anticipated.
Editor/KOKO
