A research report by Zheshang Securities stated that with the implementation of the medical insurance payment catalog policy and the accelerated expansion into overseas markets, the industry is expected to transition from its early development stage into a phase of rapid growth. The implementation of the medical insurance payment catalog policy in 2026 will clarify the fee framework for four types of robots, significantly lowering the threshold for hospital adoption. Leading enterprises such as MicroPort and Jingfeng have seen rapid growth in overseas orders, with globalization becoming a new growth driver. It is projected that by 2032, the market size of China’s surgical robot industry will surge from 7.2 billion yuan in 2024 to 76.7 billion yuan, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 34%.
The domestic surgical robotics industry is at a critical turning point, transitioning from 'proof of concept' to 'scaled profitability.'
On January 21, Zheshang Securities noted in its latest research report that with the implementation of the National Healthcare Security Administration's pricing catalog policy and the accelerated expansion into overseas markets, the industry is expected to enter a rapid growth phase from its early development stage. If the past five years were a period of technological catch-up, then the next five years will be a phase of commercial realization.
 Zheshang Securities stated that the market size for China’s surgical robotics industry will be approximately RMB 7.2 billion in 2024. According to forecasts, this figure will surge to RMB 76.7 billion by 2032, implying a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 34% over the next eight years—a growth rate that is extremely rare in the current macroeconomic environment.
Zheshang Securities stated that the market size for China’s surgical robotics industry will be approximately RMB 7.2 billion in 2024. According to forecasts, this figure will surge to RMB 76.7 billion by 2032, implying a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 34% over the next eight years—a growth rate that is extremely rare in the current macroeconomic environment.
The research report noted that on January 20, 2026, the National Healthcare Security Administration issued the 'Guidelines for Establishing Surgery and Treatment Support Procedures (Trial),' which clarified the pricing framework for surgical robots, significantly lowering the barriers for product adoption in hospitals. At the same time, leading companies have seen rapid growth in overseas orders: MicroPort Robot’s global orders exceeded 160 units, while Jingfeng Medical Technology secured 72 overseas orders. Overseas expansion is becoming a new growth driver.
Market Potential: Over RMB 70 billion scale, with annual growth of 34%
The research report indicated that according to Frost & Sullivan data, the market size for China’s surgical robotics industry will grow from RMB 7.2 billion in 2024 to RMB 76.7 billion by 2032, reflecting an approximate CAGR of 34%.
By comparison, the global market will grow from USD 21.2 billion to USD 75 billion during the same period, with a CAGR of around 17%. The growth rate of the Chinese market is significantly higher than the global average.
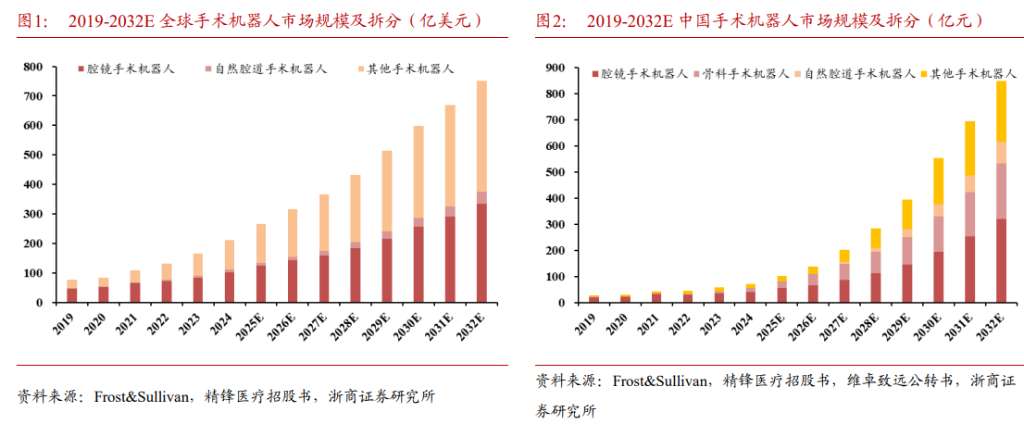
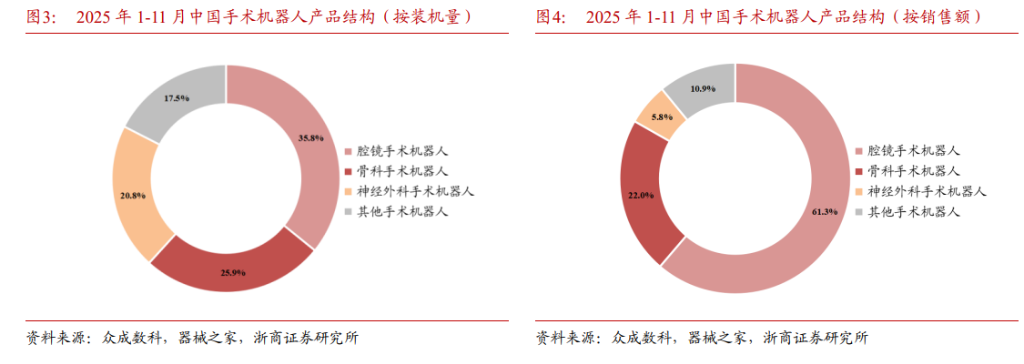
The research report highlighted that endoscopic surgical robots account for half of the market share, with endoscopic surgery robots representing 58% of the overall market size in 2024, making it the largest sub-sector.
The relaxation of licensing requirements and the implementation of the pricing catalog will serve as significant drivers. Zheshang Securities estimates that from 2024 to 2032, the market size will achieve a CAGR of approximately 29%, reaching RMB 32.1 billion by 2032.
Additionally, the orthopedic surgical robotics market ranks second only to endoscopic robotics. According to statistics from JoinData for January to November 2025, orthopedic robots accounted for 26% of total installations and 22% of sales revenue.
The research report states that with the improvement of domestically produced products and the implementation of the pricing catalog, the compound annual growth rate of the market scale from 2024 to 2032 is expected to reach 41%, reaching RMB 21.3 billion by 2032.
Key catalyst in 2026: Pricing policies to resolve hospital entry challenges
According to the research report, 2026 will be a decisive moment for policy implementation as the question of 'who will pay' is about to be systematically resolved.
The research report notes that in the past, the promotion of domestic robots faced difficulties, with the core issue being that hospitals did not consider economic viability. Only by clarifying the pricing catalog and medical insurance reimbursement ratios can social benefits be translated into economic benefits for hospitals. The 'Guidelines for Surgical and Treatment Auxiliary Operation Projects (Trial)' published by the National Healthcare Security Administration on January 20, 2026, serves as a key signal.
The development of domestically produced surgical robots can be divided into three stages:
- Early development phase: Weak product capabilities, low market acceptance, unclear clinical advantages, difficulty in pricing and hospital entry, limited deployment in leading hospitals, mainly bringing social benefits rather than economic returns.
- Rapid growth phase (beginning in 2026): Two key prerequisites have been met:
First, there is a significant improvement in product capabilities, with some manufacturers launching well-graded products recognized by clinicians.
Second, the pricing catalog has been clarified.
The pricing guidelines issued by the National Healthcare Security Administration on January 20, 2026, classify surgical robots into four categories: navigation, auxiliary execution, precision execution, and remote surgery, with additional charges based on a certain percentage of the primary procedure cost. This will significantly accelerate the adoption of these products in hospitals.
- Comparison of charging policies across regions: In 2021, Shanghai included four types of surgical procedures in Category B of medical insurance, with patients paying 20% out-of-pocket; Beijing included orthopedic robotic surgeries in Category A for full reimbursement in 2021, with associated consumables reimbursed at 70%; Hunan imposed a 40%-300% surcharge on surgical prices in 2022 but excluded them from medical insurance. The establishment of a nationwide charging framework will provide guidance for regional implementation.
Accelerating Overseas Expansion: New Growth Engine Ignites
According to research reports, China's surgical robotics market accounted for only about 5% of the global market in 2024, leaving vast opportunities in overseas markets. Leading domestic companies are rapidly expanding their global presence:
MicroPort Robotics: The laparoscopic surgical robot Tumai received CE certification in May 2024. As of December 2025, global commercial orders exceeded 160 units, covering more than 40 countries.
The orthopedic robot Honghu has obtained certifications from China's NMPA, the U.S. FDA, and the EU CE. By the first half of 2025, cumulative global orders surpassed 55 units. The proportion of overseas revenue has been continuously increasing from a low level in 2022.
Jingfeng Medical: The laparoscopic surgical robot MP1000 received CE certification in March 2025, while SP1000 received CE certification in October 2025.
As of the end of October 2025, overseas orders totaled 72 units, accounting for 61% of the global total of 118 units. The share of overseas revenue is rising rapidly.
Zheshang Securities notes that domestic companies are leveraging product quality, cost-effectiveness, and unique innovations like 5G-enabled remote surgeries to tap into overseas markets. Overseas growth is expected to be significant by 2026, potentially becoming a sustained driver of new growth.
Profit Model: Following Intuitive Surgical’s playbook, earning profits through consumables
Research reports indicate that surgical robots fundamentally operate under a 'razor-and-blades' business model. Specifically:
Benchmarking Intuitive Surgical: This giant, with a market value exceeding 187 billion US dollars, provides a standard answer. Selling equipment (systems) is just making friends; the real profit comes from the continuous stream of consumables and services thereafter. In 2024, consumables and service revenue accounted for 76% of Intuitive Surgical's total income.
Zheshang Securities believes that domestic companies must follow this logic—first deploy equipment to gain a foothold, then rely on consumables to generate profits. At this stage, the installed base is the key leading indicator. Whoever gets their machines into operating rooms first will control the cash flow valve for the next decade.
Meanwhile, the research report points out that, referring to overseas giants like Stryker Corp, the endgame for orthopedic robots is the synergy between 'equipment and implants.' The precise positioning of robots can drive the sales of high-value orthopedic consumables, which will be the key to profit recovery for domestic orthopedic giants.
